Comprises modules for describing quantum systems. More...
Namespaces | |
| freesystem | |
| Contains some typedefs for structures of arity 1 for convenience in defining free systems. | |
| lindblad | |
| Tools for describing a single Lindblad operator. | |
| time | |
| Comprises tools related to the description of different time-dependence levels. | |
Classes | |
| class | Averaged |
| The interface every system that calculates and displays quantum averages must present towards the trajectory drivers. More... | |
| class | AveragedCommon |
| The template-parameter independent base of Averaged. More... | |
| class | AveragedTimeDependenceDispatched |
| Implements the general Liouvillean interface by dispatching the two possible time-dependence levels. More... | |
| struct | AveragesNumberMismatchException |
| Exception for LiouvilleanAveragedCommonRanked::average. More... | |
| class | ClonableElementAveraged |
| Besides being an ElementAveraged, it models the Clonable concept More... | |
| class | DynamicsBase |
| Provides services for dealing with frequency-like parameters, both real and complex, for all elements, frees and interactions alike, which are hence all derived from this class. More... | |
| class | ElementAveraged |
| An implementation of Averaged for the case when the number of quantum arevages is known @ compile time (which is very often the case with elements)… More... | |
| class | ElementLiouvillean |
| An implementation of Liouvillean for the case when the number of Lindblads is known @ compile time (which is very often the case with elements)… More... | |
| class | ElementLiouvillean< RANK, 1, IS_TIME_DEPENDENT > |
| A specialization of ElementLiouvillean for the case of a single Lindblad. More... | |
| class | ElementLiouvilleanAveragedCommon |
| Implements LiouvilleanAveragedCommon::displayKey and LiouvilleanAveragedCommon::nAvr with the help of a cpputils::KeyPrinter. More... | |
| struct | ElementLiouvilleanException |
| Thrown if the Lindblad index is not smaller than the total number of Lindblads. More... | |
| class | ElementLiouvilleanStrategies |
| Besides ElementLiouvillean, this is another solution based on the strategy idiom to control the number of Lindblads @ compile time. More... | |
| class | Exact |
| The interface every system that needs transformation between two quantum mechanical pictures must present towards the trajectory drivers. More... | |
| class | ExactCommon |
| The template-parameter-independent base of Exact. More... | |
| class | ExactTimeDependenceDispatched |
| Implements the general Exact interface by dispatching the two possible time-dependence levels. More... | |
| class | Free |
In the language of the framework, a free system is a unary system (arity 1, RANK=1) More... | |
| class | FreeExact |
| A unary implementation of Exact assuming that the operator that transforms between the pictures is diagonal. More... | |
| class | Hamiltonian |
| The interface every system having (possibly non-Hermitian) Hamiltonian time-evolution must present towards the trajectory drivers. More... | |
| class | HamiltonianTimeDependenceDispatched |
| Implements the general Hamiltonian interface by dispatching the different time-dependence levels. More... | |
| struct | InfiniteDetectedException |
| Exception for LiouvilleanAveragedCommonRanked::average. More... | |
| class | Interaction |
| Describes interaction of Free elements. More... | |
| class | Liouvillean |
| The interface every system having Liouvillean time-evolution must present towards the trajectory drivers. More... | |
| class | LiouvilleanAveragedCommon |
| The template-parameter independent part of LiouvilleanAveragedCommonRanked. More... | |
| class | LiouvilleanAveragedCommonRanked |
| Common functionality of Liouvillean & Averaged. More... | |
| struct | LiouvilleanAveragedTag_ |
| A tagging struct corresponding to LiouvilleanAveragedTag. More... | |
| class | LiouvilleanTimeDependenceDispatched |
| Implements the general Liouvillean interface by dispatching the two possible time-dependence levels. More... | |
| class | NoTime |
| Describes no-time dependence corresponding to the case NO_TIME. More... | |
| class | OneTime |
| Describes one-time dependence corresponding to the case ONE_TIME. More... | |
| class | QuantumSystem |
| The abstract interface every system has to present towards the quantum trajectory drivers quantumtrajectory::MCWF_Trajectory, quantumtrajectory::EnsembleMCWF, and quantumtrajectory::Master. More... | |
| class | QuantumSystemWrapper |
| A wrapper for Exact, Hamiltonian, Liouvillean, and Averaged. More... | |
| class | TwoTime |
| Describes two-time dependence corresponding to the case TWO_TIME. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef LiouvilleanAveragedTag_< LA_Li > | LA_Li_tagType |
| typedef LiouvilleanAveragedTag_< LA_Av > | LA_Av_tagType |
| typedef blitz::TinyVector< bool, 3 > | SystemCharacteristics |
Enumerations | |
| enum | LiouvilleanAveragedTag { LA_Li, LA_Av } |
| Enumeration describing a (compile-time) choice between Liouvillean & Averaged. More... | |
| enum | TimeDependence { TWO_TIME, ONE_TIME, NO_TIME } |
| Enumeration of different possibilities for time dependence of Hamiltonians. More... | |
Functions | |
| template<int RANK, bool IS_TIME_DEPENDENT> | |
| ClonableElementAveraged< RANK, IS_TIME_DEPENDENT > *const | new_clone (const ClonableElementAveraged< RANK, IS_TIME_DEPENDENT > &cea) |
| template<int RANK> | |
| std::ostream & | display (boost::shared_ptr< const Averaged< RANK > > av, double t, const quantumdata::LazyDensityOperator< RANK > &matrix, std::ostream &os, int precision) |
| template<int RANK> | |
| const LiouvilleanAveragedCommon::DArray1D | average (typename LiouvilleanAveragedCommonRanked< RANK >::Ptr ptr, double t, const quantumdata::LazyDensityOperator< RANK > &matrix) |
Variables | |
| const LA_Li_tagType | LA_Li_tag |
| const LA_Av_tagType | LA_Av_tag |
Comprises modules for describing quantum systems.
Among them the most important is QuantumSystem, which is an abstract interface every system has to provide to be usable with quantum trajectories like quantumtrajectory::MCWF_Trajectory or quantumtrajectory::Master. This is why all the elementary and composite systems are more or less directly derived from QuantumSystem.
Much of the design here depends on the requirements of a step of the Monte-Carlo wave function method, as described in Description of the MCWF method, so the reader is asked to have a look at there, too.
Most of the classes in this namespace belong to a single hierarchy, sketched below. This diagram is however approximate, because the picture in reality is somewhat complicated by the heavy use of templates, partial specializations, and conditional inheritance. The broken lines signifying that the inheritance is not direct, due to some classes in between, which can be considered implementation details.

We have also indicated how classes representing elementary free subsystems (Mode) and interactions (JaynesCummings), and those representing composite systems (BinarySystem and Composite) fit into the hierarchy.
These modules in the hierarchy provide a lot of services for implementing new elements in the framework. For examples on how to optimally use these services, the structure-bundle guide.
Enumeration describing a (compile-time) choice between Liouvillean & Averaged.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| LA_Li | |
| LA_Av | |
Definition at line 20 of file LiouvilleanAveragedCommon.h.
Enumeration of different possibilities for time dependence of Hamiltonians.
With 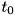 being the time instant where the two pictures coincide (cf. quantumtrajectory::QuantumTrajectory::getT0):
being the time instant where the two pictures coincide (cf. quantumtrajectory::QuantumTrajectory::getT0):
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| TWO_TIME |
Case 1 |
| ONE_TIME |
Case 2 |
| NO_TIME |
Case 4 |
Definition at line 19 of file TimeDependence.h.